Global Labor Market Insights with AI
Analysis of how AI reshapes jobs, wages, and productivity worldwide, plus industry trends and practical steps for businesses to adopt AI and upskill staff.

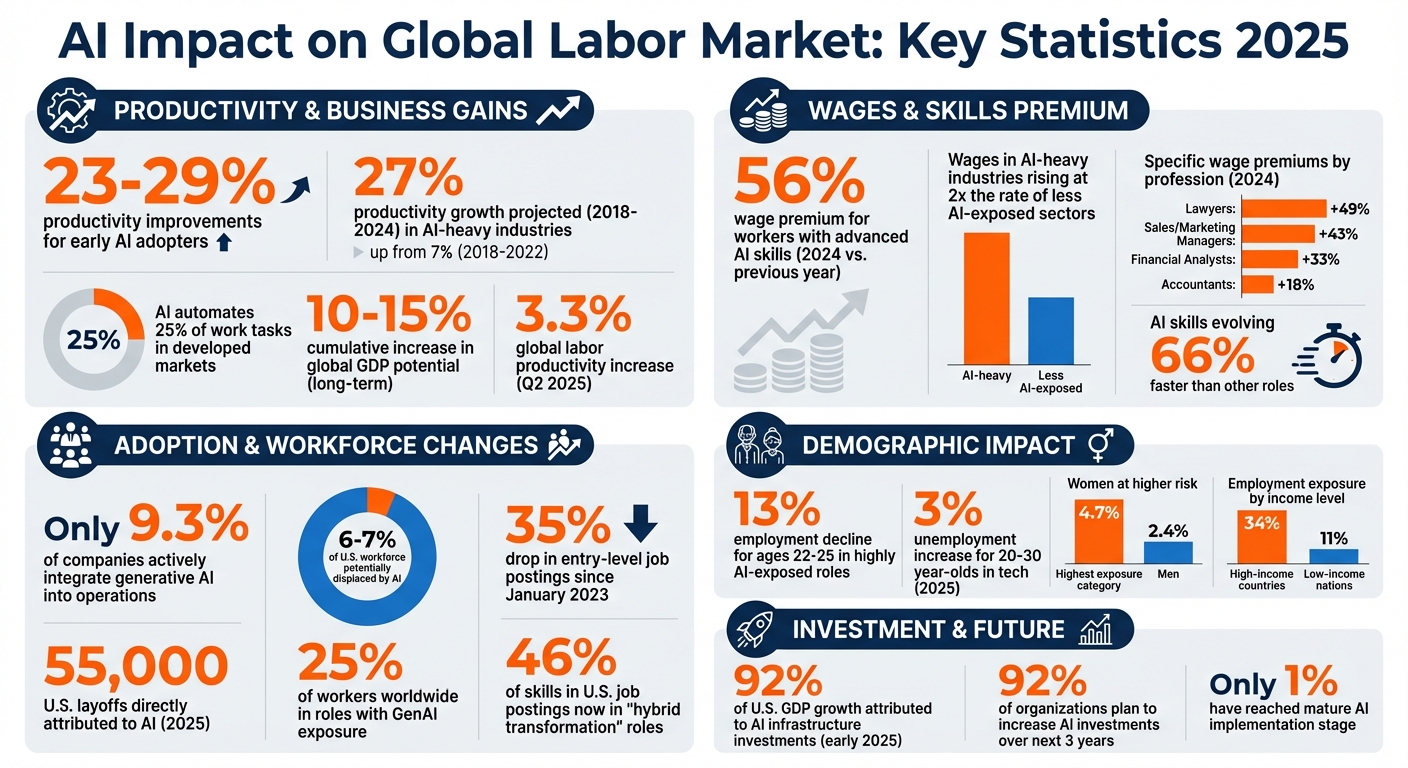
AI is transforming the global labor market, but its effects are far from uniform. By 2025, industries heavily adopting AI reported productivity gains of 23-29%, while workers with advanced AI skills saw a remarkable 56% wage premium compared to the previous year. Yet, only 9.3% of companies actively integrate generative AI into operations, signaling untapped potential and challenges for businesses navigating this transition.
In this article, you'll discover:
- How AI is reshaping workforce dynamics, including task-level automation and its impact on job roles.
- Key trends in wages and productivity, with data-driven insights into sectors experiencing the most growth.
- Practical steps for businesses, from workforce training to scaling AI adoption for measurable ROI.
These insights are grounded in real-world examples, including PwC’s analysis of 1 billion job postings and industry leaders’ strategies for leveraging AI effectively.
With AI adoption accelerating, understanding its impact is critical for staying competitive. Whether you're a business leader or workforce planner, this article offers actionable strategies to navigate these changes. Read on to explore how AI is shaping the future of work and what it means for your organization.
AI Impact on Global Labor Market: Key Statistics 2025
The Great Skill Shift: How AI Is Transforming 70% Of Jobs By 2030
Productivity and Business Benefits from AI
As AI reshapes the way we work, its impact on productivity and compensation highlights a fundamental shift in global labor trends. The adoption of AI is driving measurable progress in productivity and revenue across various sectors. Industries like financial services and software publishing, which have embraced AI, are undergoing changes comparable to past major technological revolutions. These advancements are not only boosting productivity but also redefining income dynamics and workforce roles.
Labor Productivity Increases from AI
Early adopters of AI are already seeing significant gains. Reports indicate productivity improvements ranging from 23% to 29%. In industries heavily influenced by AI, productivity has surged - quadrupling from a 7% growth rate between 2018 and 2022 to an impressive 27% growth projected for 2018 to 2024.
This remarkable increase is largely due to AI's ability to automate about 25% of work tasks in developed markets while simultaneously enhancing human capabilities. Instead of simply speeding up existing workflows, AI allows employees to focus on more valuable, strategic responsibilities. Joe Atkinson, Global Chief AI Officer at PwC, captures this shift well:
AI is amplifying and democratizing expertise, enabling employees to multiply their impact and focus on higher-level responsibilities.
Industries that have integrated AI are also seeing their revenue per employee outpace less AI-exposed sectors. Over a ten-year span, AI has the potential to boost annual U.S. productivity growth by 1.5 percentage points. Goldman Sachs estimates that, in the long run, AI could drive a cumulative 10% to 15% increase in global GDP.
Revenue Growth and Higher Wages in AI-Enabled Industries
AI's influence extends beyond productivity, with significant effects on wages and revenue. Workers equipped with AI skills are commanding notable wage premiums. In 2024, U.S. professionals with AI expertise saw dramatic increases in earnings: lawyers earned 49% more, sales and marketing managers received a 43% boost, financial analysts gained 33%, and accountants earned 18% more compared to peers without AI skills.
Wages in AI-heavy industries are rising at twice the rate of those in less AI-exposed sectors. Carol Stubbings, Global Chief Commercial Officer at PwC, highlights the broader significance:
This research shows that the power of AI to deliver for businesses is already being realised. And we are only at the start of the transition. As we roll out Agentic AI at enterprise scale, we are seeing that the right combination of technology and culture can create dramatic new opportunities to reimagine how organisations work and create value.
However, the rapid pace of AI development presents challenges. Skills in this field are evolving 66% faster than in other roles, making it critical for companies to invest in ongoing training. Pete Brown, Global Workforce Leader at PwC, underscores this need:
Even if they can pay the premium required to attract talent with AI skills, those skills can quickly become out of date without investment in the systems to help the workforce learn.
Recognizing this, businesses are prioritizing AI training as a key component of their growth strategies, ensuring their workforce remains equipped to adapt to the ever-changing demands of AI-driven industries.
Job Losses and Workforce Changes from AI
The rise of AI is reshaping employment landscapes, driving productivity and wage growth while altering hiring trends. In 2025, AI directly contributed to approximately 55,000 layoffs in the U.S.. Estimates suggest that AI could displace 6% to 7% of the U.S. workforce. However, with only 9.3% of companies actively using generative AI in regular production as of mid-2025, the full extent of its impact remains unclear.
Rather than conducting large-scale layoffs, many companies are adopting a "leaner" approach to restructuring. For instance, Amazon eliminated 14,000 corporate roles in 2025 as part of its strategy to integrate generative AI into operations. Similarly, Microsoft cut 9,000 positions, bringing its total layoffs to around 15,000 that year. Salesforce reduced its customer support team from 9,000 to 5,000, with AI now handling up to 50% of the company's workload. These examples highlight how businesses are adapting their workforce strategies in response to AI advancements.
Current Data on Job Displacement
AI's impact on employment is particularly noticeable in industries where repetitive cognitive tasks can be automated. Fields like marketing consulting, graphic design, office administration, and call centers are now experiencing slower employment growth compared to historical trends. AI has the potential to perform tasks affecting 11.7% of the U.S. labor market, potentially saving $1.2 trillion in wages across professional services.
The degree of disruption varies significantly across industries. Sectors such as wholesale trade, retail trade, finance and insurance, educational services, and real estate face high exposure to AI-driven changes. In contrast, industries like management, mining, government, and agriculture remain relatively insulated. Ford CEO Jim Farley offered a stark outlook:
AI will replace literally half of all white-collar workers in the U.S.
Meanwhile, MIT Professor Daron Acemoglu provided a more tempered perspective:
If AI pervasively goes into an automation direction, there will be fewer jobs. There'll be some job creation, but not enough
What sets this wave of AI-driven job displacement apart is its focus on reducing hiring rather than mass layoffs. For example, entry-level job postings in the U.S. have dropped by approximately 35% since January 2023. CrowdStrike CEO George Kurtz explained this approach in May 2025 while announcing a 5% workforce reduction:
AI flattens our hiring curve, and helps us innovate from idea to product faster. It streamlines go-to-market, improves customer outcomes, and drives efficiencies
Beyond the numbers, AI is also reshaping the demographic composition of the workforce.
Demographic Changes in the Workforce
AI's influence is particularly evident among early-career workers. Employment for individuals aged 22-25 in highly AI-exposed roles has declined by 13% since generative AI became widespread. Tasks like financial modeling, analysis, and basic coding, which traditionally served as stepping stones for young professionals, are increasingly being handled by AI.
The tech sector has been hit especially hard. Unemployment among 20- to 30-year-olds in tech-related roles rose by nearly 3% in 2025, a rate significantly higher than the sector average. Since November 2022, tech employment as a share of the overall workforce has steadily declined, falling below pre-pandemic levels. Researchers have dubbed these early-career workers in AI-exposed fields the "canaries in the coal mine", as they represent the first wave of structural changes in the labor market.
Gender disparities further complicate the picture. Women are at greater risk of job transformation due to their concentration in clerical and administrative roles, which are highly susceptible to automation. Globally, 4.7% of female employment falls into the highest AI exposure category, compared to 2.4% for men. In high-income countries, the gap widens significantly, with 9.6% of women in high-risk roles versus 3.5% of men.
Geography also plays a key role. High-income countries, with their highly digitized economies, experience greater exposure to AI-driven changes. In these countries, 34% of employment is exposed to generative AI, compared to just 11% in low-income nations. This creates a divide, with developed economies feeling the immediate effects of AI disruption, while developing countries face different challenges in adapting to these shifts.
AI's Impact on Specific Industries
AI is reshaping the global economy, but some sectors are feeling the effects more intensely than others. Industries like technology and professional services are undergoing significant transformations, where AI is not just about cost-cutting but fundamentally altering workflows and the value placed on certain skills. These changes highlight how AI is redefining operations across these fields.
Changes in Tech and Professional Services
The technology sector is seeing a major shift as businesses move from traditional software development to AI-driven processes. Large tech companies have made significant adjustments to prioritize AI. As Beth Galetti, Senior VP at Amazon, remarked:
This generation of AI is the most transformative technology we've seen since the Internet... we're convinced that we need to be organized more leanly.
Professional services are also evolving, though the impact varies by role. Jobs in business, finance, architecture, and engineering have seen reductions of 2% to 2.5% over five years as AI takes over routine analytical tasks. High-paying positions like management analysts and computer research scientists have experienced a 3.5% decline. In roles where AI can handle most tasks, the share of jobs has dropped by about 14%.
However, not all roles are shrinking. Legal jobs, for instance, are expected to grow by 6.4%, despite AI automating document-related tasks. Human oversight remains critical to avoid errors and provide nuanced advice that AI cannot replicate. Lawrence D. W. Schmidt, Associate Professor of Finance at MIT Sloan, explained:
Firms that adopt AI don't necessarily need to shed workers; they can grow and make more stuff and use workers more efficiently than other firms.
Interestingly, productivity gains from AI have benefited high-wage roles. These positions have grown by 3% over five years, and companies heavily adopting AI report 6% higher employment growth and 9.5% more sales growth over the same period. This trend shows that AI can create new opportunities even as it automates routine work.
As industries adapt, the demand for new skills and shifts in pay scales are becoming inevitable.
New Skill Demands and Pay Rates
AI is reshaping job roles by emphasizing specific skills and adaptability. In industries heavily influenced by AI, wages are rising at twice the rate of those less affected. Workers with AI expertise are earning substantial premiums across all sectors.
The focus of many roles has shifted from performing routine tasks to managing AI outputs - overseeing results, addressing complex cases, and ensuring quality control. Nearly half (46%) of skills listed in U.S. job postings now fall into "hybrid transformation" roles, where humans validate AI-driven execution. In software development, this figure jumps to 81%.
Emerging skills like AI oversight, prompt engineering, and managing system complexity are becoming highly valuable. At the same time, human-centric abilities - such as emotional intelligence, empathy, and real-time decision-making - are gaining importance as AI handles more routine cognitive tasks. Annina Hering and Arcenis Rojas from Indeed Hiring Lab highlighted this shift:
The real question is not whether GenAI will change jobs - it absolutely is, and will. The question is what kinds of jobs will be most and least changed, why, and how.
The job market reflects these changes. Roles paying over $57,000 annually added approximately 3.5 million jobs between 2019 and 2022, while lower- and middle-wage positions declined. STEM job growth has accelerated, from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% by 2024. Employers are increasingly valuing demonstrated skills and hands-on experience, with 60% of U.S. workers possessing valuable, experience-based skills rather than formal credentials.
| Occupation | Projected Growth (2023–33) | Primary AI Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Software Developers | +17.9% | Enhancement: AI assists with coding, testing, documentation |
| Personal Financial Advisors | +17.1% | Mixed: Robo-advisors compete; humans handle complex planning |
| Database Architects | +10.8% | Enhancement: System integration and predictive analysis |
| Lawyers | +5.2% | Enhancement: Document synthesis and legal research |
| Paralegals | +1.2% | Automation: High exposure in document review |
| Credit Analysts | -3.9% | Automation: AI synthesizes financial data for credit scores |
| Claims Adjusters | -4.4% | Automation: AI plus drones assess damage automatically |
| Insurance Appraisers | -9.2% | Automation: Software-driven damage estimation |
The message from PwC's 2025 Global AI Jobs Barometer is clear:
Workers with AI skills command significant wage premiums, with every analyzed industry paying higher wages for AI capabilities.
For businesses, the path forward lies in upskilling employees and strategically using AI to enhance, rather than replace, human contributions. This approach sets the stage for sustainable growth in an increasingly AI-driven economy.
What's Next for AI and the Global Workforce
The pace of AI-driven changes is accelerating, reshaping industries in the span of just a few business cycles. Currently, one in four workers worldwide - 25% - are in roles that involve some level of exposure to Generative AI. The decisions being made today are laying the foundation for the workforce of the future. This transformation emphasizes a key point: AI is not about replacing humans but about building systems where humans and AI collaborate effectively.
Business Opportunities in an AI-Driven Economy
The economic influence of AI is undeniable. In early 2025, investments in AI infrastructure were responsible for an impressive 92% of U.S. GDP growth, prompting upward revisions to growth forecasts. Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell highlighted this trend, stating:
AI spending on data centers, and related [things], has been holding up business investment... AI spending will continue.
The adoption of AI tools is also on the rise, with 70% of technology companies using paid AI solutions compared to just 40% in other industries. This surge in AI-driven productivity contributed to a 3.3% global labor productivity increase in the second quarter of 2025. The International Labour Organization further noted:
Because of the continued need for human input, most jobs will be transformed rather than made redundant.
These developments present a clear opportunity for businesses willing to invest wisely in both technology and their workforce. To fully realize these opportunities, companies must refine their strategies for scaling AI adoption.
Practical Steps for Implementing AI
While many companies recognize the potential of AI, there’s often a gap between planning and execution. Although 92% of organizations intend to increase AI investments over the next three years, only 1% have reached a mature stage in AI implementation. Bridging this gap requires bold leadership and well-defined strategies.
A key starting point is preparing the workforce. Many executives are focusing on retraining their current employees - an average of 32% of the workforce - rather than hiring new talent, which accounts for 23% of their efforts. Microsoft's Jared Spataro captured this shift, stating:
Productivity is becoming less about headcount and more about how effectively humans and agents work together.
Recent success stories illustrate the potential of AI integration. In April 2025, Wells Fargo deployed an AI agent across 4,000 branches to assist 35,000 bankers with retrieving customer information. This system handled 75% of queries, cutting response times from 10 minutes to just 30 seconds. Similarly, Bayer's Crop Science R&D team used AI to manage data-heavy tasks, saving researchers up to six hours per week.
For businesses looking to implement AI effectively, three steps stand out. First, establish structured AI training programs - 48% of employees believe formal training is the best way to encourage adoption. Second, focus on high-impact use cases that enhance daily tasks and enable innovative workflows. Third, create a workplace culture where employees feel empowered to innovate with AI without fearing job displacement.
Additionally, companies are rethinking traditional organizational structures. Leading firms are moving away from conventional "Org Charts" and adopting "Work Charts", where flexible human-agent teams are formed around specific objectives. This shift requires new metrics to determine the ideal balance between human oversight and AI efficiency for different tasks.
FAQs
How can businesses use AI to increase productivity and drive revenue growth?
To make the most of AI, businesses should begin by pinpointing tasks where data and human effort overlap - think repetitive workflows or decision-making processes that could benefit from automation. AI has the potential to simplify operations, deliver actionable insights, and improve decision-making, freeing up employees to focus on more creative and strategic responsibilities.
A smart first step is to test AI in areas with high potential impact, such as sales prospecting or customer engagement. Starting with clean, well-organized data is crucial. If improvements in speed or accuracy become evident during this trial phase, businesses can then expand AI applications to other functions. For instance, AI platforms like RINDA can automate tasks such as identifying international buyers, crafting multilingual personalized outreach, and analyzing performance metrics. These capabilities not only help businesses scale globally but also improve overall efficiency.
To ensure long-term success, employees must be trained to work alongside AI. Research highlights that businesses combining AI with human oversight often experience notable increases in productivity and revenue, with global economic benefits from AI integration projected to hit $13 trillion by 2030. By aligning AI's strengths with business objectives, companies can streamline operations, make better use of their resources, and drive measurable growth.
What skills are most in demand for jobs in AI-driven industries?
The most in-demand skills in AI-driven industries blend technical know-how with strong communication and problem-solving capabilities. Employers are placing a high value on expertise in areas such as machine learning, data analysis, AI product design, and prompt engineering, which are often associated with higher salaries. For instance, professionals skilled in AI product design can earn a notable wage premium in the U.S.
Furthermore, proficiency in human-AI collaboration is becoming increasingly critical. This includes managing AI-enhanced workflows, applying ethical AI practices, and integrating AI tools into existing processes. Excelling in these roles requires a combination of technical expertise - like fine-tuning models and managing data pipelines - and soft skills, such as multilingual communication, stakeholder engagement, and creative problem-solving. Together, these abilities help harness AI's potential in industries like sales and operations.
How is AI transforming job roles and employment trends across industries?
AI is reshaping workplaces across a wide range of industries, with generative AI leading the charge in how tasks are performed and roles evolve. Research indicates that around 26% of jobs could experience major changes, while another 54% may undergo moderate adjustments as businesses integrate AI technologies and employees acquire new skills. Many positions are transitioning into what’s being called "hybrid transformations", where AI tools assist with tasks, but human expertise and oversight remain essential.
The degree of impact depends on the sector and an individual's career stage. Entry-level roles in areas like customer support, data entry, and routine analytics are more susceptible to change, as these tasks are often repetitive and easier to automate. On the other hand, experienced professionals tend to enjoy greater job stability. Industries such as manufacturing and logistics, which rely heavily on repetitive processes, are more exposed to automation. Meanwhile, knowledge-intensive sectors like finance and legal services are incorporating AI as a tool to enhance efficiency rather than replace human workers.
Rather than eliminating jobs outright, AI is transforming them, highlighting the growing demand for skills that combine technical expertise with critical thinking and human judgment. For both businesses and employees, the priority lies in adapting to these "hybrid transformations" and preparing for a labor market that’s becoming increasingly dynamic due to AI-driven advancements.
Related Blog Posts
- Going global: 10 frequently asked questions and answers
- AI Sales Agents Replace 10,000+ Jobs in July - Is Your Sales Team Next?
- Global Expansion in 2025: Why 56% of US Startups Are Betting on AI-Powered International Growth
- Why 70% of CPG Manufacturers Choose AI Over Cost-Cutting: Rockwell's 2025 Industry Report Reveals Strategic Shift
