AI in Partner Selection for Emerging Markets
AI cuts partner search from months to days, reduces supplier risk, and improves match rates in emerging markets using multi-agent systems and localized data.

AI is transforming how businesses approach partner selection in emerging markets. Traditionally, sourcing professionals spent over three months and 40+ hours manually evaluating a limited pool of candidates, exposing businesses to risks and missed opportunities. Now, AI-powered tools can analyze millions of potential partners in hours, improving efficiency and decision-making. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, AI tools helped a regional government identify 30 suppliers in under a week, doubling testing capacity in just a month.
In this article, you'll discover:
- How AI reduces partner search time by over 90%, enabling faster market entry and improved scalability.
- The role of AI in mitigating risks, such as over-reliance on single suppliers, with up to a 50% reduction in exposure.
- Emerging trends like hierarchical multi-agent systems, which improve partner match rates by 10–15%.
As businesses increasingly expand into emerging markets, leveraging AI tools is no longer optional. With 60% of respondents in these regions trusting AI for partner selection, compared to 40% in advanced economies, the time to act is now. Read on to learn how your business can capitalize on AI-driven insights to build stronger, data-focused partnerships.
How AI Changes Partner Selection
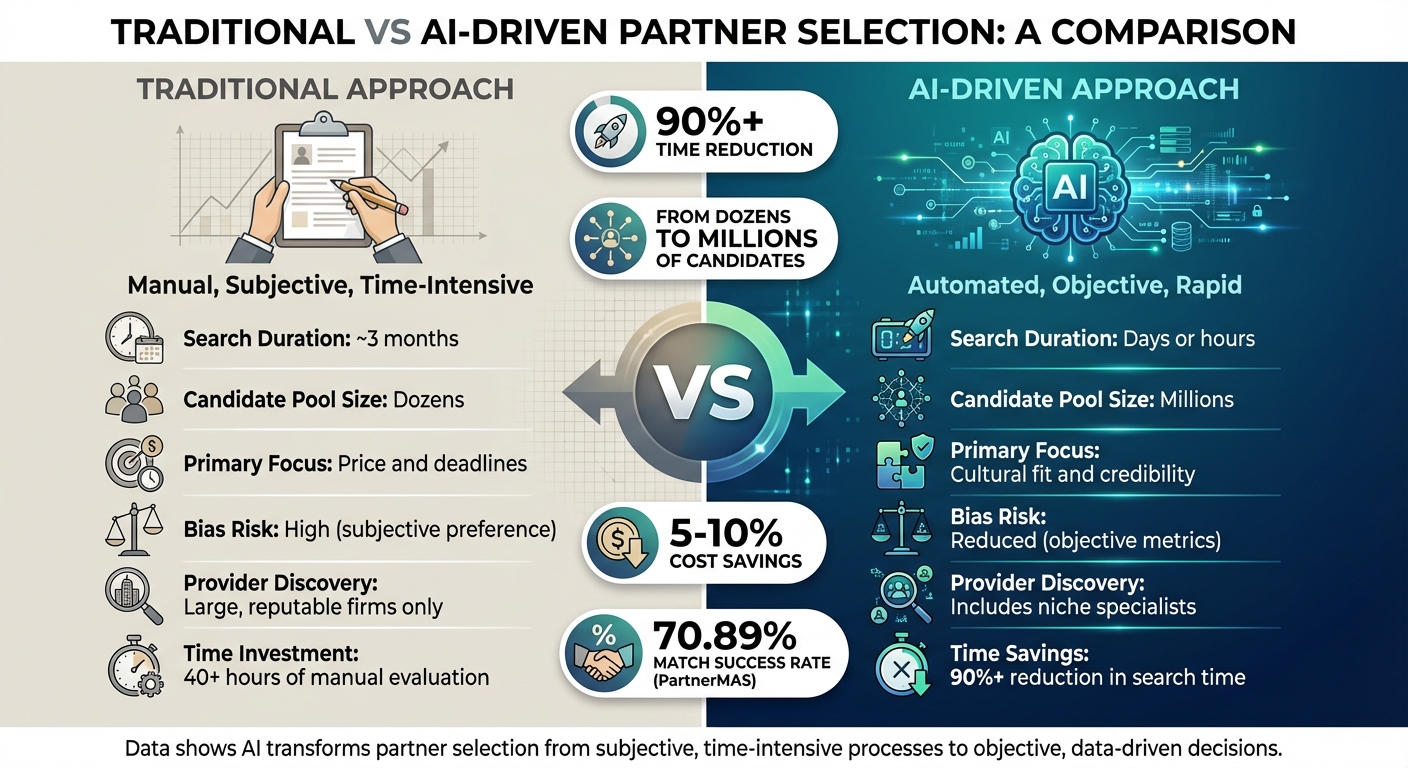
Traditional vs AI-Driven Partner Selection: Speed, Scale and Efficiency Comparison
Challenges in Traditional Partner Selection
For years, businesses have struggled with inefficiencies in finding reliable partners, particularly in emerging markets. Traditional selection methods often focus narrowly on price and deadlines, overlooking crucial factors like cultural compatibility and strategic alignment. This narrow focus can lead to what some call "reputation fixation", where procurement teams gravitate toward large, well-known firms, ignoring smaller, specialized providers that might offer better terms or innovative solutions.
Another significant challenge is the reliance on manual processes. Sourcing professionals typically evaluate only a small fraction of potential candidates - often just a few dozen from thousands - due to time constraints and limited resources. This process is further complicated by subjective biases and personal preferences, which can cloud judgment. In regions where transparency is scarce, these limitations often result in partnerships that fail to meet strategic goals.
Cultural and linguistic differences add yet another hurdle. Traditional Request for Proposals (RFPs) rarely account for communication nuances or cultural compatibility, both of which are essential for successful partnerships. Without a systematic way to verify credibility in opaque markets, businesses often find it difficult to separate trustworthy partners from opportunistic ones.
AI offers a way to tackle these inefficiencies head-on, shifting the process from subjective decision-making to data-driven insights.
Benefits of AI-Driven Partner Selection
AI is transforming the partner selection process by addressing these challenges with speed and accuracy. For instance, Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables procurement teams to describe their needs in plain language, while AI algorithms can scan millions of global suppliers in just hours - a task that used to take months. A noteworthy example is PartnerMAS, a hierarchical multi-agent framework developed in 2025 by Lingyao Li from the University of South Florida and Haolun Wu from McGill University. This system achieved a 70.89% success rate in identifying co-investment partners across 140 real-world cases, outperforming single-agent models by about 15% while also cutting token costs.
By replacing subjective evaluation with data-driven analysis, AI brings a level of objectivity that traditional methods lack. AI tools can assess supplier profiles, client reviews, and pricing while also analyzing cultural and linguistic compatibility using NLP. This reduces "familiarity bias", which often leads companies to stick with known partners, and helps uncover niche providers that manual searches might miss. Businesses leveraging advanced AI-driven supplier discovery report cost savings of 5% to 10%.
The table below highlights the stark contrast between traditional and AI-driven approaches:
| Feature | Traditional Approach | AI-Driven Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Search Duration | ~3 months | Days or hours |
| Candidate Pool Size | Dozens | Millions |
| Primary Focus | Price and deadlines | Cultural fit and credibility |
| Bias Risk | High (subjective preference) | Reduced (objective metrics) |
| Provider Discovery | Large, reputable firms only | Includes niche specialists |
Perhaps one of AI's most impactful contributions is its ability to continuously verify trust in markets with limited transparency. Instead of relying solely on reputation or past collaborations, AI systems can autonomously monitor performance indicators and conduct real-time credibility checks. This capability is particularly valuable in emerging markets, where 60% of respondents trust AI for partner selection, compared to just 40% in advanced economies.
Research and Insights on AI in Emerging Markets
World Bank and OECD Report Findings
Global research continues to shed light on how AI is shaping emerging markets, highlighting both opportunities and challenges. Recent findings from the World Bank and OECD uncover a striking paradox in AI adoption. By mid-2025, over 40% of ChatGPT's global traffic stems from middle-income countries like Brazil, India, Indonesia, and Vietnam. Yet, high-income nations dominate the AI landscape, controlling 87% of advanced AI models and 91% of venture capital funding, despite representing just 17% of the world’s population.
The World Bank's "Four Cs" framework - Connectivity, Compute, Context, and Competency - emerges as a critical foundation for AI-driven business partnerships. However, these studies reveal significant disparities. In low-income countries, fewer than 5% of people have basic digital skills, compared to 66% in wealthier nations. Additionally, these regions account for less than 0.1% of global co-location data center capacity as of June 2025.
Despite these gaps, smaller-scale AI applications are already making a difference in developing economies. They are improving supply chains and enabling partner discovery without the need for heavy infrastructure investments. The OECD further highlights AI's role in reducing defect rates and minimizing material input requirements, both of which are essential when assessing partner reliability in global value chains. These findings set the stage for exploring emerging trends in AI-driven partner selection.
Current Trends in AI-Enabled Partner Selection
New trends are transforming how businesses in emerging markets approach partner selection, reflecting the broader global insights. Three key developments stand out:
- Hierarchical Multi-Agent Systems: These systems break down partner evaluation into specialized roles - planners, domain experts, and supervisors - leading to 10%–15% higher match rates compared to traditional methods.
- Open-Source AI for Localized Innovation: Open-source technologies are empowering emerging markets to adapt AI solutions to their specific needs. The World Bank emphasizes the importance of aligning AI with local languages, data, and realities, noting that most training data remains focused on English. However, new formats like video and audio are creating fresh opportunities for developing nations to participate in the AI ecosystem. This shift is evident as 20% of GenAI-related job openings are now located in middle-income countries.
-
Synthetic Data and Predictive Modeling: These tools are becoming essential for refining partner selection processes, though challenges related to "data maturity" and access to quality public data persist. The OECD recommends that governments provide clear frameworks to help small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) navigate AI vendor selection. As they note:
Governments could also provide guidelines or a framework to help small and medium-sized enterprises navigate the vendor selection process, indicating, for instance, important considerations to be aware of when choosing an AI vendor.
These trends illustrate how AI is not only optimizing partner selection but also adapting to the unique conditions of local markets. By moving away from subjective decision-making, businesses are building stronger, data-driven ecosystems tailored to their specific challenges and opportunities.
Case Studies: AI in Partner Selection
AI-Powered Buyer Discovery and Multilingual Communication
During the COVID-19 pandemic, a regional government faced significant bottlenecks in testing capacity. To address this issue, they turned to AI-driven procurement tools, which enabled them to identify over 30 high-potential global suppliers for swabs and viral-transport media in less than a week - a task that would typically take three months and over 40 hours of manual effort. Within two weeks, new agreements were finalized, allowing the organization to double its testing capacity within a month.
This case highlights how AI can overcome traditional limitations in search processes. Modern AI tools can analyze vast datasets, scanning millions of potential partners and delivering a refined shortlist in just hours. This efficiency reduces search time by 90% or more. For businesses venturing into emerging markets, this speed is invaluable, especially when navigating language barriers and unfamiliar regulatory landscapes.
RINDA offers a practical example of this capability, leveraging AI to automate overseas buyer discovery while supporting multilingual communication in over 20 languages. The platform not only identifies potential buyers but also verifies their interest in real time and crafts personalized outreach strategies. These features directly address challenges like those faced by the regional government, enabling businesses to expand into new markets confidently and without the delays of traditional methods.
In addition to streamlining supplier discovery, AI provides detailed local insights that enhance ongoing partnerships.
Customized Partner Insights for Local Markets
LinkedIn's sales team introduced an AI-driven Account Prioritization Engine in 2024 to help their representatives identify high-potential accounts across diverse markets. By analyzing account behavior, engagement trends, and market signals, the machine-learning model developed tailored prioritization strategies. This approach led to an 8.08% increase in renewal bookings, demonstrating how AI-driven insights can directly boost revenue in competitive markets.
These examples emphasize the value of AI in adapting partner selection to specific market conditions. Companies that integrate AI into their supply chain strategies often gain a competitive edge, achieving cost positions 5% to 10% lower than their peers. The real advantage lies in moving beyond generic searches to embrace data-driven, customized strategies. By accounting for local market dynamics, regulatory requirements, and cultural specifics, businesses can better position themselves in emerging markets where these factors are often critical.
Future of AI in Partner Selection
Opportunities for Scalability and Market Expansion
AI is paving the way for businesses to expand into emerging markets that were once considered difficult to access. By leveraging this technology, companies can skip over traditional development hurdles. Keegan Fonte, MBA '25 from Cornell University, highlights this potential:
By integrating AI, these markets can leapfrog traditional development stages, potentially accelerating economic and social progress.
The economic impact of AI is staggering. AI-powered agents and robots could contribute approximately $2.9 trillion annually to the U.S. economy by 2030. However, the global distribution of these benefits remains uneven. If current trends persist, only 3% of AI's economic advantages are projected to reach Latin America, while Africa, Oceania, and other Asian markets (excluding China) are expected to receive just 8%. This disparity underscores both the challenges and opportunities for businesses that can effectively implement AI-driven tools for partner selection in these regions.
Advanced frameworks are key to addressing these challenges. For instance, hierarchical multi-agent strategies, like those utilized in PartnerMAS, have demonstrated 10–15% higher match rates, proving their effectiveness in scaling partner selection processes. These frameworks are especially valuable in emerging markets, where fragmented data often poses significant obstacles.
Platforms such as RINDA further illustrate the potential of AI in global expansion. These tools enable companies to identify and collaborate with partners across diverse markets, overcoming barriers that have historically hindered growth in underserved regions. By streamlining partner selection, these scalable AI solutions not only support market expansion but also tackle the unique challenges of emerging economies.
Addressing Risks and Infrastructure Gaps
Despite AI's potential, it faces hurdles related to infrastructure and bias. Infrastructure challenges are particularly pronounced in some regions. For example, in Colombia, only 75% of the population has regular internet access, and just 40% own laptops. Energy constraints further complicate matters, with data center electricity consumption projected to triple by 2035.
Small Language Models (SLMs) offer a practical solution in areas with limited energy resources. These models require less than 20% of the energy consumed by standard Large Language Models, making them a viable option for delivering effective partner selection capabilities in energy-constrained environments. Strategic investments in infrastructure also play a crucial role. For instance, AWS Africa's Cape Town cloud region, which launched in 2020, contributed $673 million to South Africa's GDP by August 2025, showcasing how infrastructure development can fuel AI-driven business growth in challenging markets.
Another pressing issue is data bias. According to Terry White, Associate Chief Analyst at Omdia:
AI is useful and global. However, generic AI trained on Western models may actually inhibit development in emerging markets.
To address this, many countries are turning to Sovereign AI initiatives. These efforts focus on creating localized AI models that incorporate regional dialects and cultural nuances, ensuring that partner selection tools align with specific market needs.
Businesses can take several steps to mitigate these challenges. Establishing a Center of Excellence (COE) can help standardize AI practices and ensure analytical consistency across global operations. Encouraging regional data-sharing policies can improve access to localized training data. Additionally, prioritizing AI fluency - the ability to effectively use and manage AI tools - is becoming increasingly important as demand for this skill grows. Tackling these obstacles is essential for unlocking AI's full potential in partner selection.
How to Use AI for Partner Selection
Implementing AI Solutions Like RINDA
To effectively use AI for partner selection, businesses need structured data, a clear process, and integration with CRM or PRM systems. As Greg Portnoy points out:
AI will not help you if you do not have existing process and you do not have data.
Before introducing any AI tool, ensure your CRM or PRM systems contain well-organized data on partner interactions and deal outcomes. This foundation is critical for AI to deliver meaningful results.
Leading AI systems often rely on a three-tier hierarchical framework - Planner, Specialized, and Supervisor Agents - to boost match rates by 10–15%. This method proves especially useful in emerging markets, where fragmented data can complicate partner selection.
Platforms like RINDA simplify the process of finding the right partners. A practical approach is to start small: define your Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) and align your local tech stack for two specific target countries. Then, identify 5 to 10 local partners and set clear success metrics, such as pipeline growth or improved conversion rates. This initial application of AI lays the groundwork for a scalable, data-driven partner ecosystem.
Creating a Data-Driven Partner Ecosystem
Once AI tools are in place, the focus should shift to maintaining momentum through continuous data integration. Building a sustainable partner ecosystem isn't just about selecting the right partners initially; it requires ongoing refinement and strategic coordination. Regularly updating data helps reduce selection bias, minimize risks, and enhance operational efficiency.
Top-performing companies often assign dedicated analytics teams to manage procurement and sourcing. These teams ensure that AI systems are continuously enriched with data from internal sources, like CRM logs and spending patterns, as well as external ones, such as market databases, web mining, and social media risk profiles.
The shift from transactional partnerships to outcome-focused collaborations is reshaping how success is measured. To fully realize the benefits, adopt an orchestration mindset. This involves creating tailored workflows for different partner types and establishing clear interdepartmental handoffs.
For better visibility, tag every partner-sourced deal in your CRM to track revenue attribution. This data-driven approach enables AI to refine selection criteria, uncover successful patterns, and predict high-value partnerships. In successful programs, partners have contributed between 25% and 65% of total business revenue within just two years.
FAQs
How does AI make partner selection faster and more effective in emerging markets?
AI streamlines the process of selecting partners in emerging markets by quickly analyzing intricate data sets, including financial figures, market trends, and qualitative insights. What once took months can now be accomplished in just a few days, with accuracy and match rates improving by 10–15%.
Through automation of tasks like data analysis and pattern recognition, AI removes the need for weeks of manual work. This allows businesses to dedicate more time to strengthening partnerships and broadening their global presence with greater efficiency.
What are the potential risks of using AI for selecting business partners in emerging markets?
Using AI to select partners in emerging markets introduces certain challenges that businesses need to navigate carefully. One of the main issues lies in the quality of data these systems rely on. When data is incomplete, outdated, or carries inherent biases, the results can skew unfairly - potentially favoring some firms while ignoring others that may be just as capable. The task becomes even more complicated when AI has to process varied data formats, such as numerical figures, categorical classifications, or textual descriptions, which can sometimes lead to inconsistent or inaccurate recommendations.
Regulatory compliance is another significant hurdle. Emerging markets often have evolving legal frameworks, and AI-driven decisions that fail to account for local laws, licensing stipulations, or sanctions could result in financial penalties or damage to a company’s reputation. Additionally, there’s the risk of adversarial manipulation, where malicious actors might inject false data into the system to influence results to their advantage. Over-reliance on AI adds another layer of concern, as it can reduce critical human oversight - especially in areas like assessing cultural compatibility or understanding subtle market dynamics that algorithms might overlook.
To mitigate these risks, businesses must strike a balance by combining AI-driven insights with human judgment. Strong data governance and thoughtful integration of both machine and human expertise are key to making well-informed and reliable decisions.
What strategies can businesses use to address infrastructure challenges when implementing AI in emerging markets?
Businesses operating in emerging markets often face infrastructure hurdles such as unreliable broadband, inconsistent power supplies, and fragmented logistics networks. To address these challenges, AI solutions tailored to these environments can make a significant difference. By adopting cloud-based models that run on lightweight devices, collaborating with local telecom providers to enhance mobile connectivity, and utilizing algorithms optimized for low data usage, companies can ensure their AI systems remain operational even in areas with limited bandwidth.
Take RINDA, for instance - a global sales platform powered by AI. It automates critical functions like identifying overseas buyers, managing multilingual communication, and analyzing performance metrics. Designed to function efficiently over mobile networks, RINDA minimizes the need for extensive local IT infrastructure while offering effective tools for selecting business partners. By combining such specialized technologies with strategic local collaborations, businesses can navigate connectivity and resource challenges, making AI a practical tool for growth in emerging markets.
